Cause
:
In most cases the cause of spasmodic dysphonia is 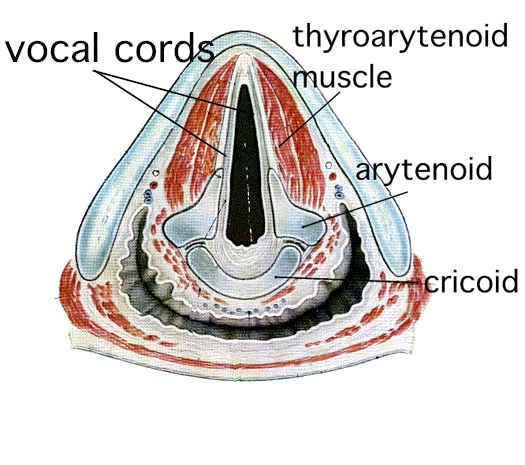 unknown. Most Medical personnel believe that Spasmodic Dysphonia is a central nervous system disorder
and a focal form of dystonia.
unknown. Most Medical personnel believe that Spasmodic Dysphonia is a central nervous system disorder
and a focal form of dystonia.
Dystonia disorders are thought to be due to abnormal
functioning in the area of the brain called the basal ganglia.The basal ganglia are structures situated deep in the brain.
The onset is usually gradual with no obvious explanation.
Researchers are investigating possible reasons why individuals suffer from Spasmodic Dysphonia including familial
factors, inflammation, and/or injury that may potentially lead to central nervous system changes in laryngeal motor control,
but none of these factors have been confirmed as a cause.
Spasmodic Dysphonia may occur with other dystonias
such as blepharospasm, oromandibular dystonia, or cervical dystonia.
S
ymptoms of Spasmodic Dysphonia :
Symptoms
of spasmodic dysphonia differ, depending on the type of the disorder.
The following are characteristics of the two different types:
1.
Adductor Type
A.
Vocal symptoms
· onset
is characterized by nonspecific hoarseness , with associated “vocal catches”-pitch and phonation breaks that eventually
evolve into complete laryngospasms
· patients
with advanced form may present with strained, squeezed staccato phonation
· extreme
phonatory effort results in little acoustic output
· vocal
symptoms are most noticeable when attempting to communicate
· laughing,
singing, non-communicative vocalizations and sometimes shouting are often unaffected
· abrupt
voice breaks
· not
intermittent- rarely goes away completely once it begins
· patients
may report a good voice for brief periods upon awakening, and when they are extremely relaxed, as when drinking alcohol
· spectral
analysis
· abrupt
voice breaks,
· irregular
wide spaced vertical striations,
· some
high-frequency noise
· distinct
well preserved formants
B.
Non-vocal symptoms - these symptoms may be observed as the patient struggles to speak
· fatigue
· difficulty
breathing
· muscle
pain in the upper chest
· synkinetic
eye blinking
· exaggerated
chest and abdominal wall contractions
· bulging
neck muscles
·
bulging veins in the neck
2. Abductor Type
A. Vocal Symptoms
· abrupt
voice breaks
· intermittent
moments of aphonia and breathiness
· impairment
of voiced/voiceless phoneme distinctions
· transitions
from a voiceless consonant to a vowel in a stressed syllable is most difficult
· frequently
unable to initiate laryngeal valving following the voiceless consonant
· glottal-widening,
abductor type laryngospasm
B.
Non -Vocal Symptoms
· Breathiness
is the primary non-vocal symptom
Audio-links : http://www.dysphonia.org/

